A Comprehensive Guide for Borrowers
In today’s fast-paced world, managing finances is crucial. Whether you’re looking to buy that dream home, purchase a car, pay for higher studies, or deal with unexpected medical expenses, loans are there to help fill the financial gaps. But a common question pops up:
👉 How do lenders calculate interest rates on loans?
👉 What determines your monthly EMI amount?
Many borrowers take out loans not fully grasping how interest accumulates or why the EMI varies based on the type of loan. Understanding EMI calculation is key; it can help you:
✔ Borrow wisely
✔ Avoid unnecessary interest
✔ Pick the right lender
✔ Make better credit choices
✔ Boost your confidence as a borrower
In this guide, we’ll break everything down into simple terms:
🔹 What’s interest?
🔹 Types of interest rates
🔹 What’s EMI and how do you calculate it?
🔹 Fixed vs Floating interest
🔹 Factors influencing loan interest rates
🔹 EMI amortization (how interest and principal are divided)
🔹 Tips for reducing interest costs
🔹 Real-life illustrations and examples
Let’s dive in!
💡What is Interest?
Interest is the extra cost you pay to the lender for borrowing their money. Think of it as the rental fee for using their funds.
Example:
If you borrow ₹1,00,000 and pay back ₹1,20,000, then ₹20,000 is the interest—the cost for borrowing the money.
🏦 What are Interest Rates?
The interest rate is the percentage of the loan amount that the lender charges you annually.
📌 This determines how much extra you’ll pay on top of what you borrowed.
Interest rates can vary based on factors like:
- Type of loan (home, car, personal, business)
- Your credit score
- Loan duration
- Stability of income
- Market conditions
- Whether you have collateral
- The lender’s risk assessment
⭐ Different Types of Interest
There are primarily two types:
1️⃣ Simple Interest (SI)
This type of interest is calculated only on the original loan amount (the principal).
📌 Formula:
SI = (P × R × T) / 100
(P = Principal, R = Rate, T = Time in Years)
➡ Used for: Short-term and smaller loans
2️⃣ Compound Interest (CI)
This is where interest is charged on both the principal and any accumulated interest, making it more costly.
📌 Formula:
CI = P (1 + R/100)^T − P
➡ Common for: Most long-term loans like home, car, and personal loans
🧮 What is EMI?
EMI stands for Equated Monthly Installment.
It’s a fixed monthly payment that you make to pay off a loan over time.
📌 Your EMI covers:
- Principal (initial amount borrowed)
- Interest (cost you pay for borrowing)
This method lets borrowers pay back loans consistently and conveniently over the years.
If you want to create AI Ads you can visit: https://adscribe.online
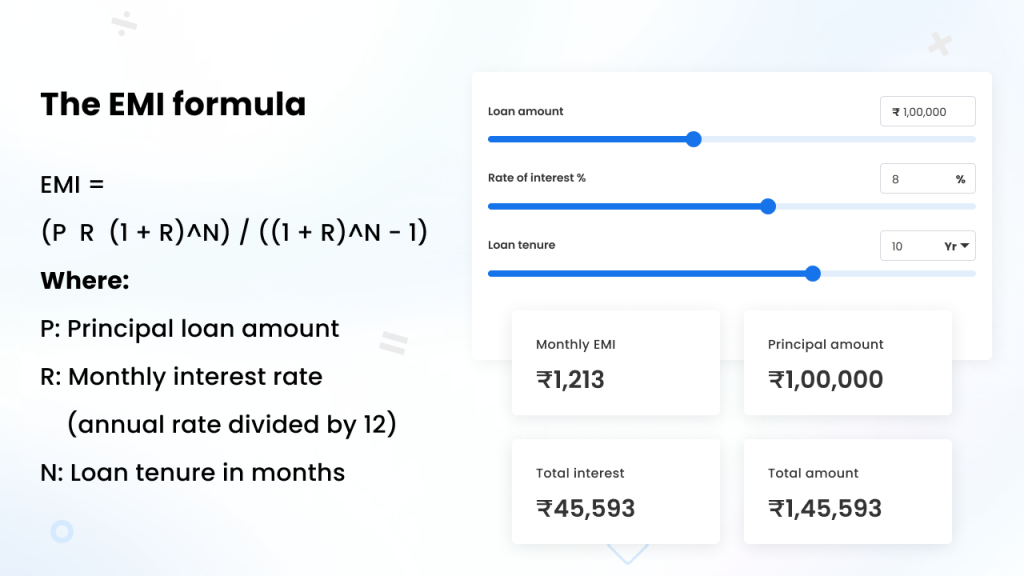
🔍 EMI Formula Explained
Most banks use the reducing balance method along with compound interest.
📌 EMI Formula:
EMI = [P × R × (1+R)^N] / [(1+R)^N − 1]
Where:
- P = Loan Amount
- R = Monthly Interest Rate = Annual Rate ÷ 12
- N = Loan Tenure in Months
📝 Example of EMI Calculation
Loan Amount: ₹10,00,000
Interest Rate: 10% annually
Tenure: 10 years (120 months)
Step-by-step:
- Annual rate = 10% → Monthly Rate = 10/12 = 0.833% = 0.00833
- N = 120
Now plug in the values into the formula:
EMI ≈ ₹13,215 per month
➡ Total repayment = ₹13,215 × 120 = ₹15,85,800
➡ Total interest paid = ₹5,85,800
📌 Even with a 10% interest rate, you end up paying almost 59% extra over 10 years!
🔻 Principal vs Interest in EMI
In the initial months:
The interest portion is higher, while the principal portion is lower.
Towards the end of the loan:
The interest decreases, and the principal repayment increases.
This breakdown appears in an Amortization Schedule.
📊 Amortization Example (First 5 Months)
| Month | EMI (₹) | Interest (₹) | Principal (₹) | Balance (₹) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 13,215 | 8,333 | 4,882 | 9,95,118 |
| 2 | 13,215 | 8,292 | 4,923 | 9,90,195 |
| 3 | 13,215 | 8,251 | 4,964 | 9,85,231 |
| 4 | 13,215 | 8,210 | 5,005 | 9,80,226 |
| 5 | 13,215 | 8,168 | 5,047 | 9,75,179 |
📌 You’ll notice you’re mainly paying interest upfront, while the principal reduces slowly.
🏠 Fixed vs Floating Interest Rates
When you’re taking a loan, you generally choose between:
🔹 Fixed Interest Rate
- Stays constant throughout the loan term
- EMIs are predictable
- Great for long-term stability
Drawback: If market rates drop, you still pay the higher rate.
🔸 Floating Interest Rate
- Fluctuates based on market conditions
- Could lighten the financial load if rates drop
- More flexible for short-term loans
Drawback: EMIs might unexpectedly rise.
🧩 Factors Influencing Loan Interest Rates
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Credit Score | Higher score → lower interest |
| Income & Employment Stability | More stability → better rates |
| Loan Amount & Tenure | Longer tenure → higher total interest |
| Collateral Security | Secured loans → cheaper rates |
| Type of Loan | Personal loans generally cost more than home loans |
| Market Conditions | Inflation & RBI policies influence rates |
| Customer Relationship | Existing customers often get better deals |
📌 Good financial behavior means less interest burden.
📌 How Credit Score Affects Interest
| Credit Score | Rating | Expected Interest |
|---|---|---|
| 750 – 900 | Excellent | Lowest |
| 700 – 749 | Good | Standard |
| 650 – 699 | Average | Higher |
| Below 650 | Poor | Very High / Loan Denied |
➡ Improving your credit score can lead to significant savings over long loans.
💥 Hidden Costs in Loans
Interest isn’t the only expense! Lenders might also charge:
- Processing Fees
- Late Payment Penalties
- Prepayment or Foreclosure Charges
- Insurance
- Documentation Fees
- Stamp Duty
📌 Always figure out the total borrowing cost before you sign anything.
💸 Why a Longer Tenure Means More Total Interest
Even if your EMI is lower, you end up paying interest for a longer period.
Example:
| Tenure | EMI | Total Paid | Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 Years | ₹21,247 | ₹12,74,820 | ₹2,74,820 |
| 10 Years | ₹13,215 | ₹15,85,800 | ₹5,85,800 |
📌 Just by doubling the tenure, you could double the interest!
📚 EMI Calculation Methods Used by Banks
| Method | Used For | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Flat Rate | Some car and consumer loans | Expensive |
| Reducing Balance | Home, car, personal loans | Cheaper |
Flat Rate Example
Loan: ₹1,00,000
Rate: 10%
Tenure: 3 years
Interest = 1,00,000 × 10% × 3 = ₹30,000
Total repayment = ₹1,30,000
Monthly EMI = ₹3,611
➡ Seems cheap at first, but you pay interest on the full amount each year, not just on the reducing balance!
Reducing Balance Method Example
Here, interest goes down as the principal decreases.
Monthly EMIs might be a bit higher, but you end up paying less in total interest.
📌 Always opt for the reducing balance method if you can.
🧠 Tips for Reducing EMI & Interest Burden
✔ Improve your credit score
✔ Compare lenders before you apply
✔ Make a larger down payment
✔ Consider a shorter tenure if you can swing it
✔ Make part-prepayments when you have extra cash
✔ Avoid late EMI payments
✔ Lower your outstanding debt before applying
✔ Go for secured loans if possible (lower risk = lower rate)
📌 Small prepayments early in the loan term can lead to big interest savings!
You can also read our other loan related blogs, please visit: https://loans.fundicainvestments.com/top-apps-online-platforms-for-loans/
🧮 Real-Life Scenario Comparison
Case Study
Loan Amount: ₹15,00,000
Interest Rate: 9%
Tenure: 15 years
| Option | EMI | Total Paid | Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard EMI | ₹15,197 | ₹27,35,460 | ₹12,35,460 |
| With Annual Prepayment of ₹50,000 | ₹15,197 | ₹21,90,000 | ₹6,90,000 |
➡ Savings = ₹5,45,460 + closure 3 years earlier!
🔍 Why EMI Calculator Tools Matter
Using online EMI calculators can be really useful:
- Help you avoid unexpected costs
- Let you choose the best EMI before getting approval
- Clarify the repayment structure
- Easily compare different banks
👉 Smart borrowers always make use of EMI calculators!
🔐 Secured vs Unsecured Loans – Interest Perspective
| Loan Type | Example | Typical Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Secured | Home loan, Gold loan | Low (7%–12%) |
| Unsecured | Personal, Credit Card loans | High (14%–40%) |
📌 More risk for the lender means higher interest for you.
📊 EMI & Interest Summary Table
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| EMI | Fixed monthly loan payment that includes both principal & interest |
| Calculation Method | Compound interest (reducing balance) |
| Early Years | More interest, less principal |
| Late Years | Less interest, more principal |
📌 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1️⃣ Why do I pay more interest at the start?
Because the principal amount is high initially, and interest is charged on the remaining balance.
2️⃣ What happens if I miss an EMI payment?
You’ll face a penalty and it could hurt your credit score.
3️⃣ Can I lower my EMI after the loan is taken?
Yes, you can do this through refinancing, extending the tenure, or restructuring.
4️⃣ Is a Zero-Interest loan genuinely zero interest?
Usually not; the interest is often hidden in the product price!
🌟 Final Thoughts
Grasping how EMI and interest calculations work gives you the power to make smart borrowing decisions. It’s not just about getting an approval for a loan, but ensuring repayments are manageable, stress-free, and financially sound.
Here’s what you should bear in mind:
✔ Shorter tenure = Less interest
✔ Good credit score = Lower rates
✔ Early repayments = Big savings
✔ Secured loans tend to be cheaper than unsecured ones
Knowledge is truly powerful in finance.
Now you’re equipped to borrow wisely!
Leave a Reply to ⭐ How Credit Score Affects Loans Approval & Interest Rate: The Ultimate Borrower’s Guide – Fundica Investments Cancel reply